Sustainable Cities: A Global Priority
Cities around the world are experiencing unprecedented growth, with over half of the world’s population—approximately 4 billion people—now living in urban areas. By 2050, this figure is projected to exceed 6.5 billion, accounting for nearly two-thirds of the global population. This rapid urbanization presents both opportunities and challenges, making the way cities handle this growth crucial for the environment.

Global Goals for Sustainable Urban Development
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development sets out 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with SDG 11 focusing on cities. This goal aims to create “inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable” urban environments. The New Urban Agenda (NUA), adopted at the 2016 Habitat III conference in Quito, Ecuador, further supports these goals with a 20-year roadmap that seeks to enhance the social, cultural, and environmental well-being of city residents.
The Role of Cities in Combating Climate Change
Urban centers play a crucial role in combating climate change. As Naoko Ishii, CEO and Chairperson of the Global Environment Facility, highlights, “The fight against climate change will be won or lost in cities.” Cities are hubs of innovation, providing a platform for collaboration among business leaders, financial institutions, planners, and regulators.
The World Bank is actively working to develop competitive, inclusive, and resilient cities, focusing on supporting the urban poor. The Sustainable Cities program significantly contributes to these efforts by fostering partnerships and driving advancements that lead to sustainable urban environments.
GEF’s Commitment to Sustainable Urbanization

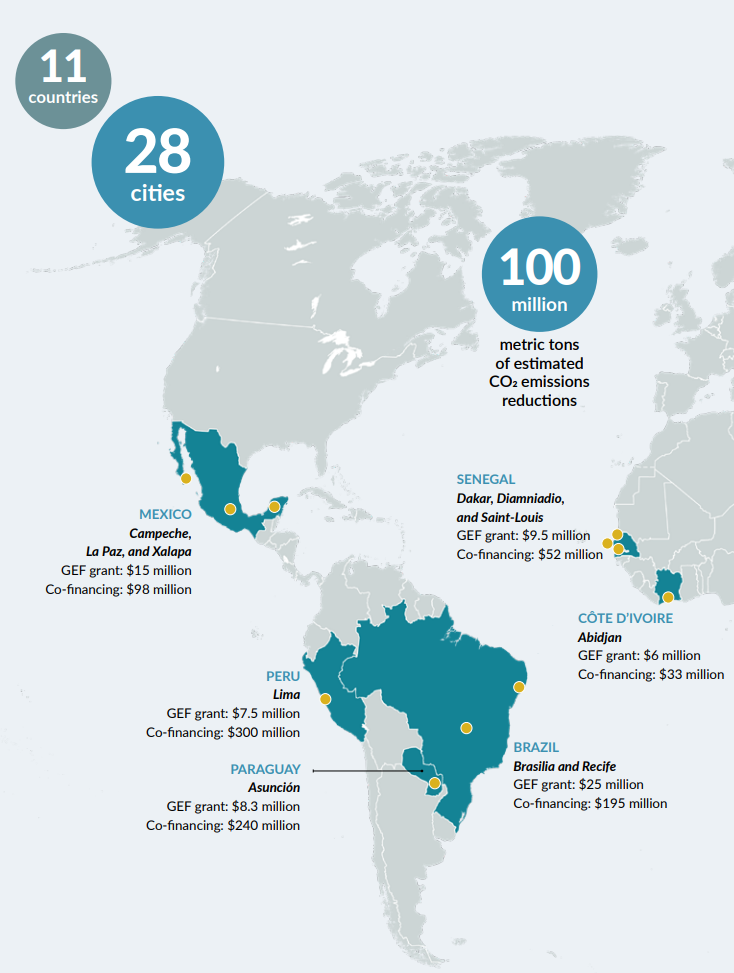
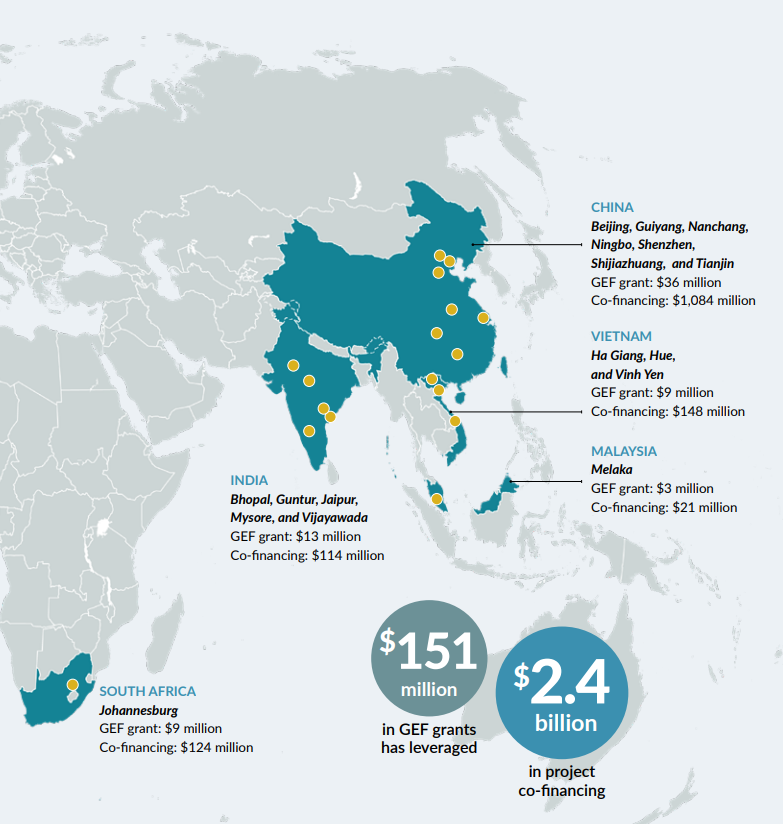
The Global Environment Facility (GEF) recognizes that well-managed cities can be drivers of a green economy, delivering significant environmental benefits. In contrast, poorly managed urban areas can lead to unplanned development, straining ecosystems, exacerbating climate change, and increasing pollution. To tackle these challenges, GEF launched the Sustainable Cities Integrated Approach Pilot under its GEF-6 funding cycle, supporting 28 cities across 11 developing countries with approximately $151 million in grant funding, and leveraging an additional $2.4 billion in co-financing.
Focus Areas of the GEF-7 Cycle

As GEF transitions to the GEF-7 cycle, the Sustainable Cities program will evolve into an impact-driven initiative that leverages emerging technologies and innovative strategies to deliver significant environmental benefits. The program will focus on the following areas:
Financial Solutions for Urban Development: Strengthening cities’ fiscal capacities and utilizing creative financing mechanisms to promote sustainability.
Evidence-Based Spatial Planning: Enhancing planning at national, regional, and local levels with geospatial tools and digital leadership.
Decarbonizing Urbanization: Promoting infrastructure integration to improve connectivity and foster innovation in transport and logistics.
Building Resilience: Developing smart systems and housing solutions to enhance energy efficiency and streamline municipal services.
| GEF-7 Focus Area | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Spatial Planning | Utilize geospatial tools and enhance digital leadership. |
| Decarbonization | Integrate infrastructure to boost connectivity and transportation innovation. |
| Resilience Building | Implement smart systems to enhance energy efficiency and resource management. |
| Financial Solutions | Develop fiscal strategies and financing instruments for sustainable urban development. |

The World Bank’s Efforts in Promoting Sustainable Communities
The World Bank has established a range of initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable communities and addressing climate change, which are crucial for eradicating poverty and fostering shared prosperity. With ambitious climate targets set for 2021–2025, the World Bank plans to double its climate finance to $200 billion, supporting 100 cities in implementing low-carbon, compact urban planning strategies. This funding is designed to integrate climate considerations into policy planning, implementation, and evaluation, significantly boosting adaptation and resilience efforts.

Investing in Game-Changing Technologies
The GEF-7 cycle continues to support projects that incorporate cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches to drive transformative environmental impacts. By harnessing both public and private resources, the program aims to maximize stakeholder engagement and deliver impactful solutions for sustainable urban development.

A Holistic Way Forward
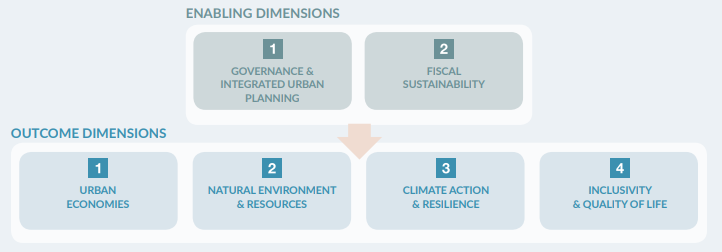
The Sustainable Cities Integrated Approach underscores the necessity for transformational change to achieve meaningful environmental impacts on a global scale. The Global Environment Facility (GEF) supports comprehensive coalitions of stakeholders, focusing on scalable activities that address pressing environmental challenges. Since 2015, the GEF-6 Sustainable Cities program has championed integrated approaches that balance urbanization’s dual roles in economic growth and environmental degradation.
Why Focus on Integrated Approaches?
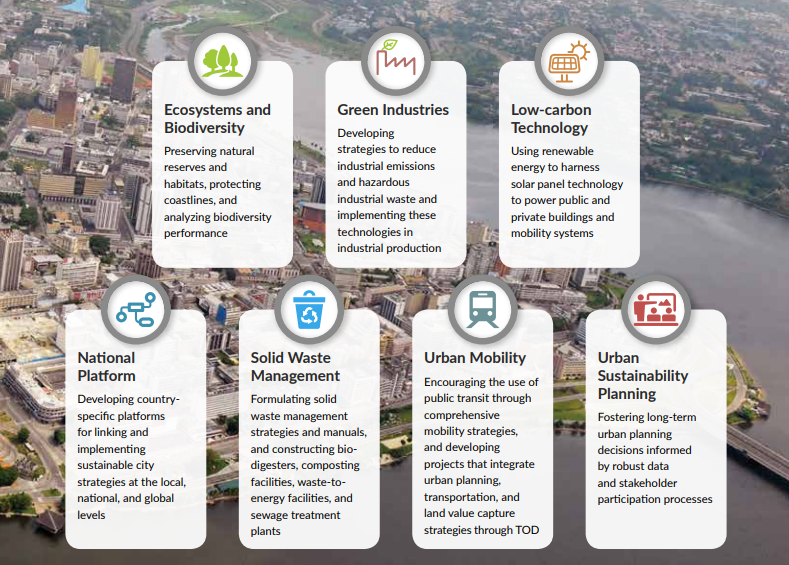
Urbanization drives economic development but also presents environmental challenges such as pollution and habitat loss. The Sustainable Cities program promotes integrated urban planning, management, and financing, which leads to resilient development and effective ecosystem management. By aligning components such as energy, transport, water, and waste management into cohesive systems, cities can achieve significant environmental benefits.
This two-track approach combines city-level projects that focus on integrated solutions with the Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC), which strategically connects these projects. This framework enables cities to become ambassadors for sustainable practices, demonstrating the power of cross-sectoral collaboration to drive transformative change.

Global Platform for Sustainable Cities—The Power of Partnership
The Global Platform for Sustainable Cities (GPSC) serves as a central hub for knowledge exchange, partnership strengthening, and the pursuit of urban sustainability. Established in 2017, GPSC unites a diverse array of cities and organizations, capitalizing on the benefits of collaboration. The platform is built around three core pillars:
Connecting Stakeholders: Encouraging partnerships among development banks, UN agencies, knowledge partners, and others to support holistic urbanization efforts.
Sharing Knowledge: Equipping cities with state-of-the-art knowledge and expertise in urban planning, management, and financing.
Capacity Development: Facilitating connections among cities and stakeholders to share best practices and insights in sustainable urban development.
GPSC’s Pillars Supporting Sustainability
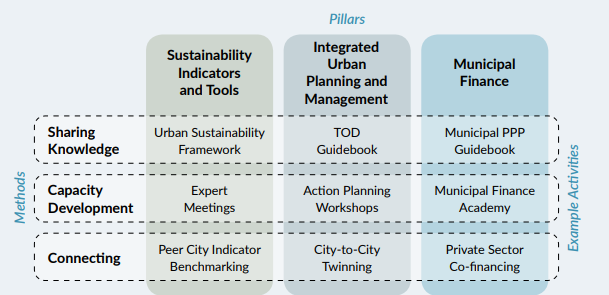
The GPSC initiatives are structured around three key pillars, each reinforced by cross-cutting engagement methods:
- Sustainability Indicators and Tools: GPSC promotes a unified approach to using indicators and tools for assessing urban sustainability, setting goals, and tracking progress. The Urban Sustainability Framework (USF) is a key resource, providing actionable tools and guidelines for cities.
- Integrated Urban Planning and Management: This pillar focuses on strategic planning informed by robust data and technology, such as transit-oriented development (TOD) and smart urban systems.
- Municipal Finance: GPSC assists cities in developing fiscal strategies to ensure financial sustainability, linking technical assistance with market-based financing options for urban infrastructure.

| GPSC Pillar | Initiatives |
|---|---|
| Sustainability Indicators | Use of indicators and tools to monitor urban sustainability and progress. |
| Integrated Planning | Strategic urban planning with data-driven approaches, including TOD and smart systems. |
| Municipal Finance | Developing fiscal strategies and market-based financing to support sustainable infrastructure. |

Capacity Development

GPSC prioritizes building connections among stakeholders to advance integrated urban sustainability. This collaborative approach dismantles silos and fosters partnerships, allowing cities to learn from each other and share knowledge. Through its website, global meetings, and working group sessions, GPSC acts as a repository of best practices and a forum for idea exchange.
Training and Expert Discussions

GPSC conducts training sessions and expert discussions on various topics, including:
Transit-Oriented Development: Aligning land use, transportation, and environmental goals through TOD strategies.
Geospatial Data: Exploring the application of geospatial data in urban planning in collaboration with the European Space Agency.
Urban Sustainability Indicators: Developing tools and frameworks for measuring sustainability.
GHG Assessment: Integrating climate considerations into urban planning.
Connecting—Leveraging the Network
As a global convening space, GPSC facilitates collaboration among cities and agencies, bringing together practitioners from both the public and private sectors to promote sustainable urban development. The platform builds a broad-based coalition supporting sustainable management, planning, and financing for cities worldwide.
Expanding Partnerships and Investment Opportunities
GPSC continues to expand its network of implementing agencies, knowledge partners, investment partners, and resource partners. By collaborating with organizations such as the World Bank, International Finance Corporation, and UN-Habitat, GPSC leverages both public and private financing opportunities to support sustainable urban projects. This collaboration equips cities with the resources and expertise needed to achieve their sustainability objectives and drive global change.